If you have a BMI higher than 30, you are more at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, and many other diseases related to obesity. You could be a candidate for weight loss surgery in Lebanon, at Advanced BMI Weight Loss Clinic if you meet any of the following criteria:
Your Body Mass Index (BMI) is equal to or greater than 40 kg/m2
Your BMI is superior to 30, and you have any of these related medical conditions:
- High Blood Pressure
- Sleep Apnea with or without CPAP machine
- Asthma
- Type 2 Diabetes
- High Cholesterol/Lipid Levels
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Joint pain (ankles, knees, hips, lower back)
- Depression
- You have failed to permanently reduce your weight using nonsurgical methods
- You have an absence of endocrine disorders that can cause morbid obesity
Fill out the Patient Questionnaire to determine if you are candidate for weight-loss surgery, and get a precise answer from the doctors.
DISCLAIMER: Bariatric surgery does not provide sustained weight loss results without appropriate follow up with a specialized team and lifestyle modifications. Please refer to our TERMS OF USE section.
Learn more about obesity and how to choose the weight loss surgery that suits you. Are you candidate for weight loss surgery?
From the book “Your Journey Out of Obesity” – Author: Dr Nagi Jean Safa
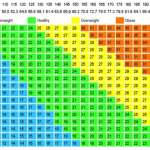
Definition of Morbid Obesity
| BMI | Classification | Health Risk |
|---|---|---|
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Normal Weight | Minimal |
| 25 – 29.9 | Overweight | Increased |
| 30 – 34.9 | Obese | High |
| 35 – 39.9 | Severely Obese | Very High |
| 40 and Over | Morbidly Obese | Extremely High |
Morbid obesity is a serious chronic illness. The blend of a genetic predisposition to gain weight, and ample and easily accessible processed food have resulted in the obesity epidemic in North America and the world. Here is a list of factors that promote the growth of morbid obesity:
- Genetic predisposition: you inherit the tendency to be obese.
- The environment: having easy access to plentiful, processed food and inability or lack of desire for vigorous physical activity.
- Psychosocial issues: being abused as a child, depression due to taunting which precipitates more eating.
- Eating disorders
- Metabolic disorders: rare medical conditions.
- Drugs: antidepressants or steroids.
- Other unknown conditions
Morbid obesity damages the body through its metabolic, mechanical and adverse physiological effects on normal bodily function. These “comorbidities” affect nearly every organ in the body in some way, and may become life threatening or may at least seriously shorten your life. Comorbidities or obesity-related health risks include:
- Cardiovascular Diseases (heart and blood vessels): Congestive heart failure, Coronary artery disease, ,Hyperlipidemia, Hypertension, Left ventricular hypertrophy, Venous stasis ulcers, thrombophlebitis.
- Endocrine (metabolic diseases): Insulin resistance, Polycystic ovary syndrome, Type 2 diabetes.
- Gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary (liver diseases): Gallstones, Gastroesophageal reflux disease, Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Genitourinary: Stress urinary incontinence, Urinary tract infection.
- Hematopoietic (diseases of the blood): Deep venous thrombosis, Pulmonary embolism.
- Musculoskeletal (diseases of bones and joints): Carpal tunnel syndrome, Degenerative joint disease, Gout, Plantar fasciitis.
- Neurologic and psychiatric: Anxiety, Depression, Pseudotumor cerebri, Stroke.
- Obstetric and gynaecologic (diseases of the female reproductive system): Foetal abnormalities and infant mortality, Gestational diabetes, Infertility (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome POS), Miscarriage.
- Pulmonary (diseases of the lungs): Asthma, Obesity hypoventilation syndrome, Obstructive sleep apnea, Pulmonary hypertension.
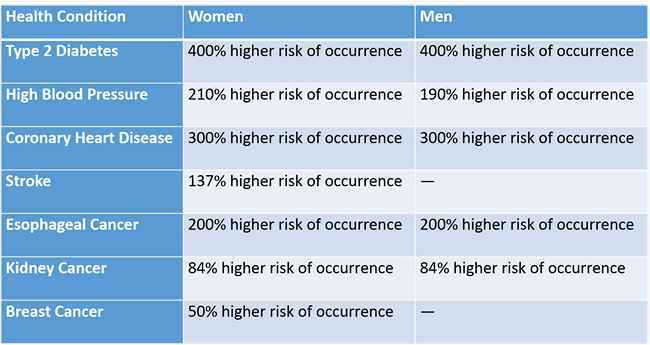
Health Risks of Morbid Obesity
The table below presents relative risks. Relative risk compares how likely an event is to occur to one person versus another. The rates show how much more likely a person with morbid obesity is to develop cancer or die from cancer in comparison with someone with a healthy weight.
MORBID OBESITY, IF UNTREATED, IS ALSO ASSOCIATED WITH A HIGHER RELATIVE RISK OF DEATH:
- Women have 50 – 100% higher mortality (death) rates than women with a healthy weight, including 62% higher cancer mortality rate.
- Men have 50-100% higher mortality rates than those with a healthy weight, including a 52% higher cancer mortality rate.
Current Bariatric (Weight-Loss) Surgical Procedures
THE CURRENT ACCEPTED BARIATRIC SURGERIES ARE SEPARATED BY TYPE INTO THREE CLASSES:
- Restrictive Procedures (Procedures in which the surgeon creates a small stomach pouch that limits the amount of food patients can eat): 1- Adjustable Gastric Banding (AGB) 2- Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (VSG) 3- Gastric Plication (LGCP)
- Combined Restrictive and Malabsorptive Procedures: Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGBP)
- Malabsorptive Procedures (Procedures in which the surgeon reroutes the small intestine so that food skips a portion of it, reducing the amount of calories and nutrients that are absorbed): 1- Biliopancreatic Diversion (BPD) 2- Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPDDS)