WHAT IS TYPE 2 DIABETES
Diabetes, or Diabetes Mellitus, is a disease whereby a person has high blood sugar, either because cells do not respond to the insulin produced, or the body does not produce enough insulin. Diabetes in Lebanon is a widespread disease, often associated with obesity.
THE THREE MAIN TYPES OF DIABETES:
- Type I Diabetes: This results from the body’s inability to produce insulin, and the person therefore requires insulin injections.
- Gestational Diabetes: This refers to when women who have never previously had diabetes have high blood glucose levels during pregnancy. It can precede the development of Type 2 Diabetes.
- Type 2 Diabetes: This is the result of insulin resistance, whereby cells fail to properly use insulin. It is often combined with a total insulin deficiency. This very common form of diabetes is diagnosed by showing any of the following symptoms: a- Fasting plasma glucose level ≥ 7.0 mmol/L (126 mg/dL). b- Plasma glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL) two hours after a 75 g oral glucose load as in a glucose tolerance test. c- Symptoms of hyperglycemia and casual plasma glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL). d- Glycated hemoglobin (Hb A1C) ≥ 6.5%.
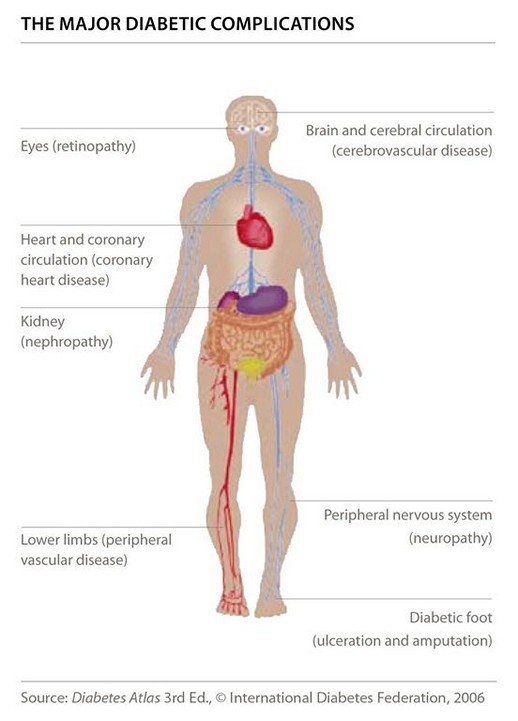
Without proper treatment, Type 2 Diabetes can be responsible for some very serious long-term health problems, such as:
- Diabetic Retinopathy: this is a major cause of blindness.
- Diabetic Nephropathy: this is a major cause of kidney failure.
- Diabetic Neuropathy: this is a major cause of non-traumatic amputations of lower extremities.
- Stroke: Without treatment for type 2 Diabetes, it becomes two to four times more likely that you will have a stroke.
- Cardiovascular Disease: A staggering eight out of ten people with type 2 Diabetes die from cardiovascular disease.
TREATMENT FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES
The first lines of treatment for Type 2 Diabetes are usually lifestyle changes. These include following a healthy diet, losing excess weight, and engaging in a regular exercise routine. If these lifestyle changes do not alter the situation, medications are prescribed. Some medications help the body use the insulin that it produces more efficiently, while others help the pancreas produce more insulin. If there is no relief with these medications, then the person may be required to take insulin. Unfortunately, these treatments for diabetes do not always work and the person is then susceptible to serious long-term complications.
Even with controlled medical treatments, many patients will still require dialysis, may lose one or more limbs, and have a heart attack, a bad reaction to drugs, or other complications. It is certainly not correct that medical therapy is without risk.